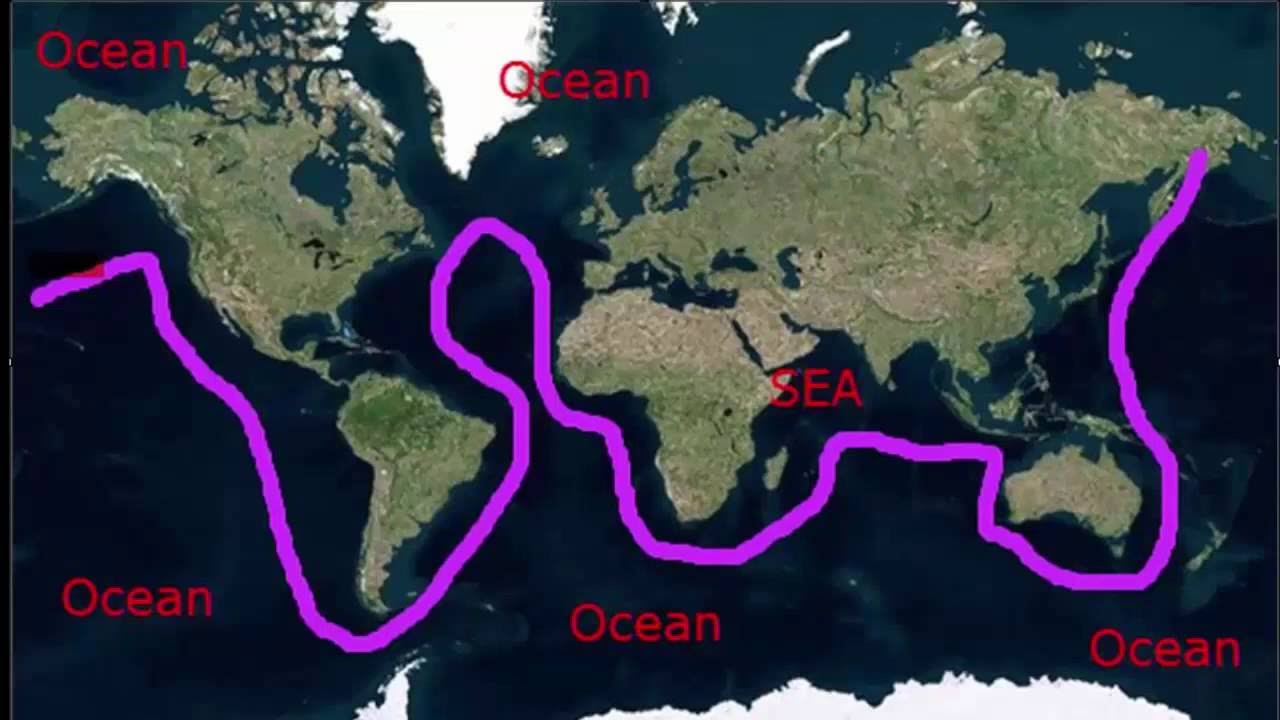
When it comes to the vast blue expanses of our planet, the terms 'sea' and 'ocean' are often used interchangeably, yet they hold distinct meanings that are crucial to understanding our world's geography. Each has its unique characteristics, significance, and role in the ecosystem. While both are bodies of saltwater, they differ in size, depth, and ecological dynamics. This article delves into the differences between seas and oceans, exploring their unique features, importance, and the fascinating life forms that inhabit them.
In a world dominated by water, it's essential to grasp the unique attributes of these two entities. Seas are generally smaller and partially enclosed by land, while oceans are vast bodies of saltwater that cover more than 70% of the Earth’s surface. Understanding the distinctions can enhance our appreciation of marine environments and the various ecosystems they support. Moreover, recognizing the vital role they play in regulating the planet's climate and weather patterns is crucial for environmental awareness and conservation efforts.
As we dive deeper into the sea versus ocean comparison, we will uncover the various dimensions of both bodies of water. From their ecological importance to their cultural and economic significance, this exploration will provide insights into why it matters to differentiate between the sea and ocean. So, prepare to embark on an enlightening journey through the waves and currents that define our planet's aquatic realms.
What Are the Key Differences Between Sea and Ocean?
Seas and oceans, while both vital parts of our planet's water systems, have several key differences that set them apart:
- Size: Oceans are significantly larger than seas, covering vast expanses of the Earth.
- Depth: Oceans are deeper, with the average depth of oceans being around 12,080 feet compared to the shallow nature of most seas.
- Boundaries: Seas are often partially enclosed by land, whereas oceans are vast, open bodies of water.
- Salinity: The salinity levels can vary, with seas sometimes having a higher salinity due to evaporation.
How Do Seas and Oceans Impact Climate?
Both seas and oceans play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate. The vast waters store heat from the sun and distribute it across the globe. Oceans, due to their size and depth, have a more significant impact on climate patterns. They help to moderate temperatures, absorb carbon dioxide, and influence weather systems, while seas can affect local climates more directly.
What Marine Life Thrives in Seas Versus Oceans?
Both seas and oceans are teeming with life, but the types of marine organisms can differ significantly between the two:
- Seas: Often host a variety of fish, mollusks, and crustaceans that flourish in shallower waters.
- Oceans: Support larger marine mammals, such as whales and dolphins, and many unique species that thrive in deeper waters.
Which Is More Accessible: Sea or Ocean?
Access to seas is often more straightforward due to their proximity to land, making them popular for recreational activities like swimming, fishing, and boating. Oceans, on the other hand, may require more extensive travel to reach, often necessitating larger vessels for exploration. This difference in accessibility influences tourism and economic activities in coastal regions.
Can Seas and Oceans Be Compared Ecologically?
Ecologically, both seas and oceans contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem health. However, seas may demonstrate more vulnerability due to their smaller size and closer proximity to human activities:
- Overfishing: Seas are often more susceptible to overfishing and habitat degradation.
- Pollution: Coastal areas experience higher pollution levels, affecting marine life.
What Are the Cultural Significances of Seas and Oceans?
Historically, seas and oceans have shaped cultures and societies. Coastal communities often have a strong connection to the sea, utilizing it for sustenance, trade, and recreation. Oceans, with their vastness, have inspired exploration and adventure, leading to significant cultural narratives and traditions around the world.
How Do Seas and Oceans Influence Global Economies?
Both bodies of water are essential to the global economy. They provide resources such as fish, oil, and minerals and facilitate trade through shipping routes:
- Fishing Industry: Seas are crucial for local fisheries, supporting livelihoods.
- Shipping and Trade: Oceans are vital for international trade, with major shipping lanes connecting continents.
Why Is Understanding the Difference Important for Conservation?
Understanding the distinctions between seas and oceans is crucial for conservation efforts. Recognizing their unique ecosystems allows for targeted protection measures to preserve biodiversity and mitigate human impacts. Conservation strategies can be more effectively implemented when we appreciate the differences and similarities between these aquatic realms.
In conclusion, the sea versus ocean debate goes beyond mere semantics. Both hold immense ecological, cultural, and economic significance, and understanding their differences can foster a greater appreciation for our planet's water bodies. As we continue to explore and learn about these vital ecosystems, we can take proactive steps to protect and preserve them for future generations.